waves unit study guide answer key
Waves Unit Study Guide: An Overview
This unit explores wave properties‚ including transverse and longitudinal types. Worksheets‚ like those from 09/25/2024‚ aid comprehension. Key concepts involve crests‚ troughs‚ and wavelength‚ supported by resources like the 07/10/2025 plugin installation guide.
Understanding Wave Properties

Delving into wave properties requires grasping fundamental concepts. Waves‚ as highlighted in available worksheets (dated 09/25/2024)‚ are disturbances that transfer energy—they don’t transfer matter itself. Understanding this distinction is crucial. Key properties include wavelength‚ the distance between successive crests or troughs‚ and frequency‚ measuring oscillations per unit time. These properties are interconnected with wave speed‚ defining how quickly the disturbance propagates.
The nature of waves dictates their behavior. For instance‚ the “Wuthering Waves” name itself evokes the dynamic energy of ocean waves‚ illustrating their inherent power. Furthermore‚ the study of acoustic waves in anisotropic media (referenced in research) demonstrates how material properties influence wave propagation.

Practical application is seen in technologies like Waves MaxxAudio‚ enhancing sound experiences on Asus systems. Successfully installing and uninstalling Waves plugins (as detailed in the 07/10/2025 tutorial) relies on understanding how these properties are manipulated within the software. Mastering these properties forms the bedrock for comprehending more complex wave phenomena.
Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal
Waves are broadly categorized into transverse and longitudinal types‚ distinguished by the direction of particle oscillation relative to wave propagation. Transverse waves‚ like those visualized in worksheets (dated 09/25/2024)‚ exhibit oscillations perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer – think of a ripple on water. They possess identifiable crests (high points) and troughs (low points).
Conversely‚ longitudinal waves demonstrate oscillations parallel to the direction of propagation. Sound waves are prime examples‚ compressing and rarefying the medium. Understanding these differences is vital‚ as they influence wave behavior. The study of waves in anisotropic media highlights how material structure impacts these wave types.

Technological applications leverage both types. Waves MaxxAudio utilizes sound waves (longitudinal) to enhance audio quality‚ while signal processing within plugins (detailed in the 07/10/2025 tutorial) often manipulates wave representations. Even the evocative name “Wuthering Waves” hints at the powerful‚ dynamic nature of wave motion‚ regardless of type. Distinguishing these types is fundamental to wave analysis.

Wave Anatomy: Crest‚ Trough‚ Amplitude‚ and Wavelength
Understanding wave anatomy is crucial for grasping wave behavior. Key components include the crest – the wave’s highest point – and the trough‚ its lowest point. These features are prominently illustrated in labeling worksheets (referenced 09/25/2024)‚ aiding visual comprehension. Amplitude defines the maximum displacement of a particle from its rest position; a larger amplitude corresponds to greater energy.
Wavelength‚ often denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ)‚ represents the distance between two successive crests or troughs. It’s a fundamental property influencing wave speed and frequency. Analyzing these elements is essential when studying wave interference and diffraction.
Furthermore‚ the characteristics of waves are impacted by the medium they travel through‚ as explored in research on anisotropic media. Software like Waves Central (installation guides dated 07/10/2025) often visually represents these wave properties during audio processing. Even the game “Wuthering Waves” evokes the imagery of crests and troughs through its name‚ highlighting the pervasive nature of wave concepts. Mastering these terms unlocks deeper wave understanding.
Wave Speed‚ Frequency‚ and Relationship
Wave speed‚ frequency‚ and wavelength are intrinsically linked. Wave speed (v) is calculated by multiplying frequency (f) by wavelength (λ): v = fλ. Frequency‚ measured in Hertz (Hz)‚ indicates the number of wave cycles passing a point per second. A higher frequency means more cycles‚ while wavelength dictates the spatial extent of one cycle.
Understanding this relationship is vital when analyzing sound waves and the electromagnetic spectrum. For instance‚ in audio plugins (mentioned in resources dated 07/10/2025)‚ manipulating frequency alters the perceived pitch. Changes in wave speed‚ influenced by the medium‚ affect how sound travels‚ as studied in anisotropic media research.
Worksheets focusing on wave properties (referenced 09/25/2024) often require calculations involving these parameters. Furthermore‚ the concept of resonance‚ where frequency matches a natural frequency‚ demonstrates this relationship’s practical implications. Even the name “Wuthering Waves” suggests the dynamic interplay of these properties. Accurate calculations and conceptual understanding are key to mastering this unit.

The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a wide range of wave types‚ categorized by frequency and wavelength. From low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays‚ each portion exhibits unique properties and applications. Understanding this spectrum is crucial‚ as it underpins technologies like MaxxAudio (mentioned 12/14/2024) which manipulates audio frequencies.

Key regions include radio waves (communication)‚ microwaves (cooking & radar)‚ infrared (heat)‚ visible light (human perception)‚ ultraviolet (sterilization)‚ X-rays (medical imaging)‚ and gamma rays (cancer treatment). Higher frequencies correspond to shorter wavelengths and carry more energy.
Wave properties within the spectrum are studied in anisotropic media (research noted)‚ impacting how waves propagate. Worksheets (referenced 09/25/2024) often require students to identify wave types and their characteristics. Furthermore‚ the development of games like “Wuthering Waves” (name reflecting wave dynamics) demonstrates an intuitive grasp of wave phenomena. Mastering the spectrum’s organization and applications is fundamental to this unit.
Sound Waves: Characteristics and Behavior
Sound waves are mechanical‚ longitudinal waves requiring a medium for propagation – unlike electromagnetic waves. Their characteristics include frequency (pitch)‚ amplitude (loudness)‚ and speed‚ influenced by the medium’s properties. Understanding these features is key‚ as demonstrated by tools like Waves MaxxAudio (12/14/2024)‚ which enhances audio perception.
Behavioral aspects encompass reflection (echoes)‚ refraction (sound bending)‚ diffraction (sound spreading)‚ and interference (constructive/destructive). These phenomena are explored through worksheets (09/25/2024) testing comprehension of wave interactions. Furthermore‚ the installation and uninstallation of Waves plugins (07/10/2025) highlight the practical application of sound wave manipulation.
The study of sound waves extends to anisotropic media‚ impacting propagation patterns. Developers like Rob Hale (mentioned alongside “Wuthering Waves”) intuitively utilize sound design principles. Analyzing sound wave behavior‚ including resonance and standing waves‚ is crucial for a complete understanding. Ultimately‚ mastering these concepts provides a foundation for advanced audio engineering and physics applications.
Factors Affecting Wave Speed
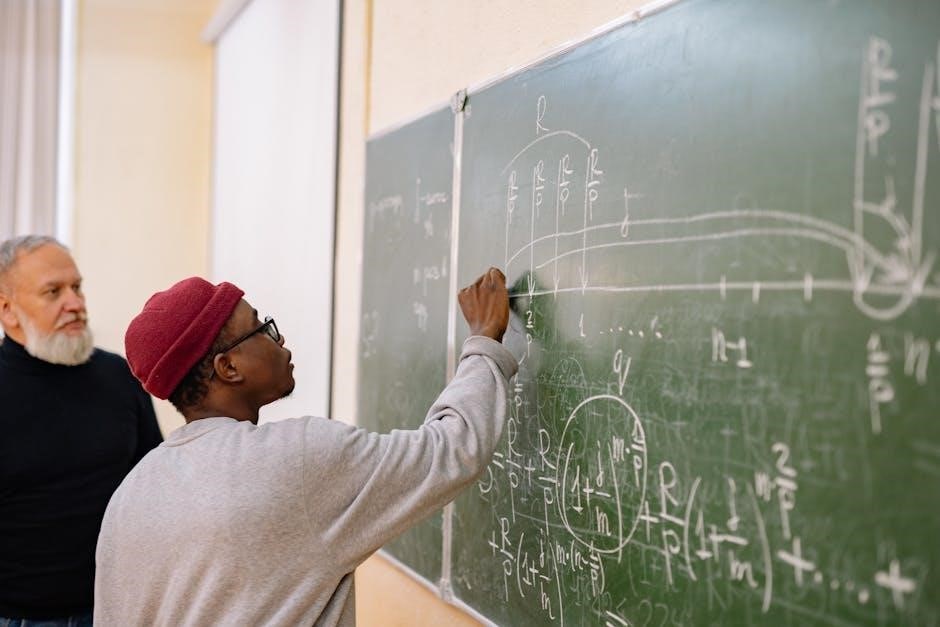
Wave speed isn’t constant; it’s profoundly influenced by the medium through which it travels. For mechanical waves‚ like sound‚ density and elasticity are primary determinants. Higher density generally decreases speed‚ while increased elasticity increases it. Electromagnetic waves‚ conversely‚ are fastest in a vacuum and slower in denser media.
Temperature also plays a significant role‚ particularly for sound waves in air. Increased temperature leads to faster molecular motion‚ thus increasing wave speed. Understanding these relationships is vital‚ as evidenced by the need for precise audio calibration using tools like Waves plugins (referenced in the 07/10/2025 installation guide).
Anisotropic media present a more complex scenario‚ where wave speed varies depending on direction‚ requiring specialized study (mentioned in research on acoustic waves). Worksheets (09/25/2024) often assess comprehension of these factors. Moreover‚ the efficient operation of software like Waves Central (for plugin management) relies on optimized data transmission speeds‚ indirectly demonstrating the importance of these principles. Ultimately‚ mastering these concepts is crucial for predicting and controlling wave behavior.
Wave Interference: Constructive and Destructive
Wave interference occurs when two or more waves overlap in the same space. This interaction results in either constructive interference‚ where waves combine to create a larger amplitude‚ or destructive interference‚ where waves cancel each other out‚ resulting in a smaller amplitude.
Constructive interference happens when waves are in phase – crests align with crests and troughs with troughs. Destructive interference occurs when waves are out of phase – a crest aligns with a trough. Understanding this principle is fundamental‚ as it explains phenomena like beats in sound and patterns in light.
Applications extend to audio engineering‚ where plugins (like those from Waves‚ detailed in the 07/10/2025 installation guide) utilize phase manipulation for effects. Furthermore‚ the optimization of audio systems like Waves MaxxAudio (mentioned 12/14/2024) relies on minimizing destructive interference. Worksheets (09/25/2024) often present scenarios to test comprehension of these concepts. Research into anisotropic media (referenced in acoustic wave studies) also considers interference patterns within complex materials. Essentially‚ interference is a core wave behavior with broad implications.
Diffraction and Refraction of Waves
Diffraction is the bending of waves around obstacles or through openings. This phenomenon is more pronounced when the wavelength is comparable to the size of the obstacle or opening. Refraction‚ conversely‚ is the bending of waves as they pass from one medium to another‚ caused by a change in wave speed.
Understanding these behaviors is crucial for explaining everyday observations‚ such as sound waves bending around corners or light bending when entering water. The degree of bending in refraction depends on the refractive indices of the two media. Diffraction also plays a role in the performance of audio systems‚ influencing sound distribution.
Applications in technology include designing lenses and acoustic diffusers. Software like Waves MaxxAudio (12/14/2024) may employ algorithms that account for diffraction and refraction to optimize sound quality. Furthermore‚ research into wave behavior in anisotropic media (acoustic wave studies) often involves complex diffraction and refraction patterns. Worksheets (09/25/2024) frequently assess understanding through diagrams and problem-solving. Plugin installations (07/10/2025) don’t directly address these‚ but the underlying principles are relevant to audio processing.
Resonance and Standing Waves
Resonance occurs when an object is vibrated at its natural frequency‚ leading to a large amplitude of oscillation. Standing waves are a special case of interference where waves reflect and superimpose‚ creating points of zero displacement (nodes) and maximum displacement (antinodes). These phenomena are intimately linked; resonance often creates standing waves.
Understanding resonance is vital in musical instruments – a guitar string resonates at specific frequencies. Similarly‚ standing waves are observed in strings fixed at both ends‚ with wavelengths determined by the string’s length. The study of wave properties (as seen in worksheets from 09/25/2024) often includes calculations related to resonant frequencies and standing wave patterns.
In audio technology‚ resonance can be both desirable and undesirable. Waves MaxxAudio (12/14/2024) aims to enhance sound‚ potentially leveraging resonant frequencies. However‚ uncontrolled resonance can cause unwanted coloration. Research into anisotropic media explores how material properties affect resonance. Plugin installation (07/10/2025) doesn’t directly cover this‚ but the principles underpin equalization and filtering. Developers like Rob Hale (mentioned in connection with Wuthering Waves) likely considered resonance in sound design.
Wave Energy and Intensity
Wave energy is the energy transported by a wave‚ directly related to its amplitude. Intensity‚ however‚ describes the power per unit area carried by the wave – essentially‚ how concentrated the energy is. Higher amplitude waves carry more energy and‚ consequently‚ have greater intensity. Understanding this relationship is crucial when analyzing wave behavior.

Worksheets focusing on wave properties (like those dated 09/25/2024) often include problems calculating energy and intensity‚ given parameters like frequency and amplitude. In sound waves‚ intensity is perceived as loudness; a louder sound has higher intensity. Software like Waves MaxxAudio (12/14/2024) manipulates audio signals to alter perceived intensity and overall sound quality.
The concept extends beyond sound. Electromagnetic waves also possess energy and intensity‚ vital in applications like radio communication and medical imaging. Plugin installation (07/10/2025) doesn’t explicitly detail energy calculations‚ but the underlying principles are essential for audio processing. Research into anisotropic media (mentioned in the provided context) may involve analyzing energy propagation in complex materials. Even game development‚ as seen with Wuthering Waves and Rob Hale’s work‚ relies on understanding energy transfer for realistic simulations.
Applications of Waves in Technology (MaxxAudio‚ Plugins)
Wave principles underpin numerous technologies‚ particularly in audio engineering. Waves MaxxAudio‚ pre-installed on some Asus systems (12/14/2024)‚ exemplifies this‚ enhancing sound quality through signal processing based on wave manipulation. Plugins‚ broadly‚ utilize wave characteristics – amplitude‚ frequency‚ phase – to modify audio signals‚ creating effects like equalization‚ compression‚ and reverb.
Understanding wave interference (constructive and destructive) is vital for designing effective audio filters. The installation and uninstallation of Waves plugins (07/10/2025) demonstrate the practical application of these concepts. These tools allow engineers to sculpt sound by selectively amplifying or attenuating specific frequencies‚ altering the wave’s shape.
Beyond audio‚ wave technology is fundamental to communication systems (radio‚ microwaves)‚ medical imaging (ultrasound‚ MRI)‚ and materials science. Even game development‚ as highlighted by Wuthering Waves and Rob Hale’s contributions‚ leverages wave physics for realistic soundscapes and visual effects. Worksheets covering wave properties (09/25/2024) provide the foundational knowledge for comprehending these advanced applications. The study of waves in anisotropic media further expands these technological possibilities.
Wave-Related Software Installation & Uninstallation (Waves Central)
Waves Central serves as the primary hub for managing Waves plugins and software‚ crucial for applying wave principles in audio production. Proper installation‚ detailed in guides from 07/10/2025‚ involves downloading the V14 offline package and running the installer‚ ensuring compatibility with your system. A pre-installation step on another computer is recommended for a smoother process.
Uninstalling Waves plugins requires meticulous attention to detail‚ as incomplete removal can cause conflicts. The process‚ outlined for both Windows and Mac‚ involves locating Waves Central‚ selecting the plugins for removal‚ and confirming the uninstallation. Manually searching for and deleting related files and registry entries is often necessary for a clean uninstall.
Understanding the underlying wave concepts – frequency‚ amplitude‚ and waveform – enhances the effectiveness of these tools. Worksheets focusing on wave properties (09/25/2024) provide the theoretical foundation. Waves MaxxAudio (12/14/2024)‚ while a pre-installed solution‚ benefits from a grasp of the wave principles it employs. Effective software management‚ via Waves Central‚ allows users to experiment and optimize their audio workflows based on these principles.

Wave Research in Anisotropic Media
Investigating acoustic waves within anisotropic media – materials with direction-dependent properties – presents complex challenges. Research‚ as noted in available documentation‚ focuses on understanding how wave propagation differs from isotropic materials. This involves studying the characteristics p(t)‚ q(t)‚ u1(t)‚ and u2(t) to model wave behavior accurately.
The motivation behind this research stems from real-world applications where anisotropic materials are prevalent‚ impacting wave transmission and reflection. Understanding these effects is crucial in fields like seismology‚ medical imaging‚ and materials science. The study of wave properties in these media requires advanced mathematical techniques and computational modeling.
Relating this back to a foundational waves unit study guide‚ understanding anisotropy builds upon core concepts like wavelength‚ frequency‚ and wave speed. While basic worksheets (09/25/2024) may not directly address anisotropy‚ they establish the groundwork for comprehending more complex wave phenomena. Furthermore‚ the principles learned are applicable even when considering software like Waves MaxxAudio (12/14/2024) operating within complex acoustic environments.
Historical Context & Developers (Wuthering Waves‚ Rob Hale)
The exploration of waves‚ both scientifically and creatively‚ has a rich history. Recent developments‚ like the game Wuthering Waves (named for the evocative imagery of surging waves – as of 02/01/2026)‚ demonstrate the continued cultural fascination with wave phenomena. The game’s title reflects core design principles‚ mirroring the power and dynamism of ocean waves.
Simultaneously‚ the loss of independent game developer Rob Hale (also known as Squid in a Box) highlights the human element behind technological and artistic innovation. Hale’s passing‚ reported in early 2026‚ impacts the potential completion of Waves 2‚ a testament to the dedication required in these fields. His work‚ like the development of audio plugins (mentioned in installation guides from 07/10/2025)‚ contributes to our understanding and manipulation of waves.
Connecting this to a waves unit study guide‚ it’s crucial to remember that these concepts aren’t purely abstract. They underpin technologies like Waves MaxxAudio (12/14/2024) and inspire creative endeavors. While worksheets (09/25/2024) focus on fundamentals‚ acknowledging the broader context – the developers and the cultural impact – enriches the learning experience.
